Just like the shape of your nose and the color of your hair and eye. Color is determined by the Genes you inherit from your parents. Those genes determined how much melanin-- a colored chemical matter -- you have in each IRIS, which is the colorful part of the eye. The more melanin you have, the darker your eyes. Less melanin makes for lighter eyes, which is why fair-skinned people often have light blue or gray eyes.
Why do I see in 3-D????
Like all human beings, you have binocular vision, both your eyes face toward the front and provide your brain with two slightly offset images. Your brain processes the differences in these two images to create a perception of depth, or a three-Dimensional view.
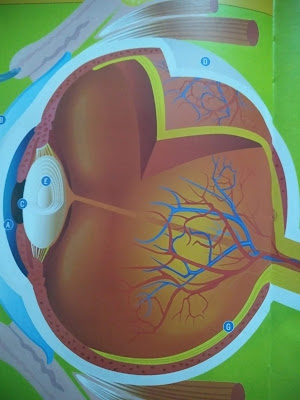
Parts of eyes and functions.
Iris: IRIS, which is the colorful part of the eye. The more melanin you have, the darker your eyes. Less melanin makes for lighter eyes, which is why fair-skinned people often have light blue or gray eyes.
Cornea: the eyes protective, transparent cover, the Corena is similar to the protective glass on a camera lens. It bends that light entering your eye to pre-focus the image before it reaches your lens.
Pupil: muscles in the iris control this hole in the center, which like a camera shutter, allows light to enter the eye and strike the lens. In bright sunlight, the pupil contracts to let in less light. In darkness, it open wide to let in as much light as possible.
Sclera: the white of our eyes, Sclera from a protective cover about the size of ping-pong ball.
Lens: like a projector in a movie theater, the lens focuses light on to the retina. It's suspended in a muscle that change the shape of the lens on focus on object near and far faster than any computerized camera.
Optic nerve : This cable carries visual information from your ratina to the brain. Your brain processes the information and translate it into what you are actually seeing.
Retina:
Why do I have eyelashes ????
These fine hair are our eyes first line of defense, shielding them from dust and dirt.
Why do I see in 3-D????
Like all human beings, you have binocular vision, both your eyes face toward the front and provide your brain with two slightly offset images. Your brain processes the differences in these two images to create a perception of depth, or a three-Dimensional view.
Parts of eyes and functions.
Cornea: the eyes protective, transparent cover, the Corena is similar to the protective glass on a camera lens. It bends that light entering your eye to pre-focus the image before it reaches your lens.
Pupil: muscles in the iris control this hole in the center, which like a camera shutter, allows light to enter the eye and strike the lens. In bright sunlight, the pupil contracts to let in less light. In darkness, it open wide to let in as much light as possible.
Sclera: the white of our eyes, Sclera from a protective cover about the size of ping-pong ball.
Lens: like a projector in a movie theater, the lens focuses light on to the retina. It's suspended in a muscle that change the shape of the lens on focus on object near and far faster than any computerized camera.
Optic nerve : This cable carries visual information from your ratina to the brain. Your brain processes the information and translate it into what you are actually seeing.
Retina:
Why do I have eyelashes ????
These fine hair are our eyes first line of defense, shielding them from dust and dirt.

No comments:
Post a Comment